WEST SYSTEM® Epoxy is a versatile, high-quality two-part epoxy that is easily modified for a wide range of coating and adhesive applications. It is used for construction and repairs that require superior moisture resistance and high strength. This guide will help you determine which products from the 105 System you need to complete your project.
1. Resin
Start with the 105 Epoxy Resin. This is the backbone of the 105 system. The 105 Epoxy Resin is meticulously designed and formulated to work alongside the WEST SYSTEM hardeners. WEST SYSTEM 105 Epoxy® is a clear, pale yellow liquid with low viscosity. WEST SYSTEM 105 Epoxy provides an excellent resin that can be applied for many applications.

2. Hardeners
Select your hardener by cure speed or select 207 if you need a clear epoxy.
| Choose by Speed | Choose Coating | |||
 |  |  |  |
|
Pot Life (100g) |
|
|
|
|
Working Time (Thin Film) |
|
|
|
|
Cure to Solid (Thin Film) |
|
|
|
|
All times given are based on working at 25°C.
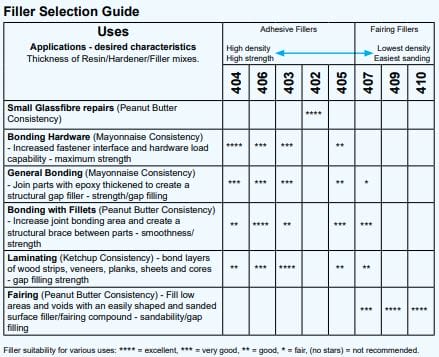
3. Fillers
Select your filler (if needed) for its handling characteristics or cured physical properties.
| Highest density | Lowest density | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Additives
Select your additive (if needed) for its handling characteristics or cured physical properties.
 |  |  |  |  |  |
|
|
|
|
|
|
You may also want to consider our reinforcing fabrics and application tools
Detailed Product Selection Information
Do you need more information to help you decide which product is right for you? Here’s a more in-depth look at factors to consider when selecting your products.
Selecting your HardenerHardener Cure Speed
Each WEST SYSTEM Epoxy resin/hardener combination will go through the same cure stages, liquid, gel, and solid. The hardener you select and the temperature you are working at will affect the rates of speed at which the mixed epoxy moves through those cure stages. Base your hardener selection on the amount of working time you’ll need for the job you’ll be doing at the temperature conditions you’ll be working under. Each hardener has an ideal temperature cure range.
The pot lifetime we provide is based on 100 grams or 4 pump strokes each of resin and hardener using our 300 Mini Pumps. If you are using a larger amount of epoxy or a different size of mixing pot, the length of pot life can vary. To increase the pot life of a cup of mixed epoxy, spread it over a larger surface area, work in a cooler environment, or mix multiple smaller batches as you go.
Epoxy Temperature
The warmer the temperature of curing epoxy, the faster it cures. The temperature of curing epoxy is determined by ambient temperature plus the exothermic heat generated by its cure.
Ambient temperature is the temperature of the air or material in contact with the epoxy. Air temperatures are most often the ambient temperature unless the epoxy is applied to a surface with a different temperature. Generally, epoxy cures faster when the air temperature is warmer and slower when it is cooler.
Hardener selection should take into consideration working temperatures in your environment.
Exothermic Heat
Exothermic heat is produced by the chemical reaction that cures epoxy. The amount of heat produced depends on the thickness and exposed surface area of mixed epoxy. In a thicker mass, more heat is retained causing a faster reaction and even more heat. The mixing container’s shape and the mixed quantity have a great effect on this exothermic reaction. A contained mass of curing epoxy (8 fl. oz. or more) in a plastic mixing cup can quickly generate enough heat to melt the cup and burn your skin. However, if the same quantity is spread into a thin layer, exothermic heat dissipates, and the epoxy’s cure time is determined by the ambient temperature. The thinner the layer of curing epoxy is, the less exothermic heat affects it, and the slower it cures.
Back to selection guide
Selecting your FillerAdhesive Epoxy Fillers
Adhesive fillers are suitable for most epoxy bonding situations, especially with high-density materials like hardwoods and metals. Adhesive filler mixtures cure to a strong, hard-to-sand-cured epoxy plastic useful in structural applications like general bonding, filleting, and hardware bonding.
Fairing Fillers
Fairing filler epoxy mixtures cure to a light, easily sandable material that is generally used for cosmetic or surface applications like shaping, filling, or fairing. Seal all faired surfaces with epoxy before painting.
Fillers can be blended to create epoxy mixtures with intermediate characteristics.
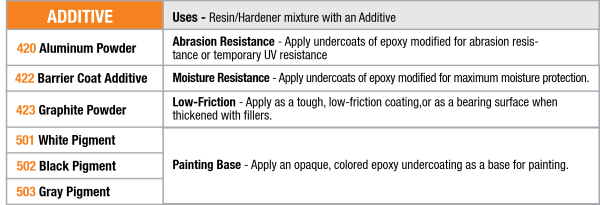
Selecting your Additives
Additives are used to give epoxy additional physical properties when used as a coating. Although additives are blended with mixed epoxy in the same two-step process as fillers, they are not designed to thicken the epoxy. Follow the mixing instructions on the container when blending these products into your epoxy resin/hardener mixture.
Aluminium Powder
420 Aluminium Powder will increase the hardness and abrasion resistance of the coated surface and improve its moisture resistance. 420 provides limited protection from ultraviolet light in areas that are not protected by other coatings and can be used as a base for subsequent painting. Cures to metallic grey colour.
Barrier Coat Additive
422 Barrier Coat Additive is a proprietary blend designed to further improve cured epoxy’s moisture exclusion effectiveness. 422 is used as a barrier coating additive to help prevent gelcoat blistering in polyester fibreglass boats and increases the epoxy’s abrasion resistance. Cures to a light grey colour.
Graphite Powder
423 Graphite Powder is a fine black powder that can be mixed with epoxy to produce a low-friction exterior coating with increased scuff resistance and durability. Epoxy/graphite is commonly used as a low-load, low-speed bearing surface. The epoxy/graphite mixture cures to black colour.
Pigments
WEST SYSTEM pigments are available in four colours, white, black, blue and grey. We suspend the pigments in an epoxy resin base which allows them to blend thoroughly into the epoxy to make very uniform colours. These are helpful to use when highlighting an epoxy-coated surface, like for fairing. Coloured surfaces highlight flaws and imperfections. It can also be used as a coloured base coat for the final finish system, like paint. Cured, pigmented epoxy surfaces are not a final finish surface but require an additional paint or UV filter coating for ultraviolet protection, so it holds up for years to come.
Back to selection guide